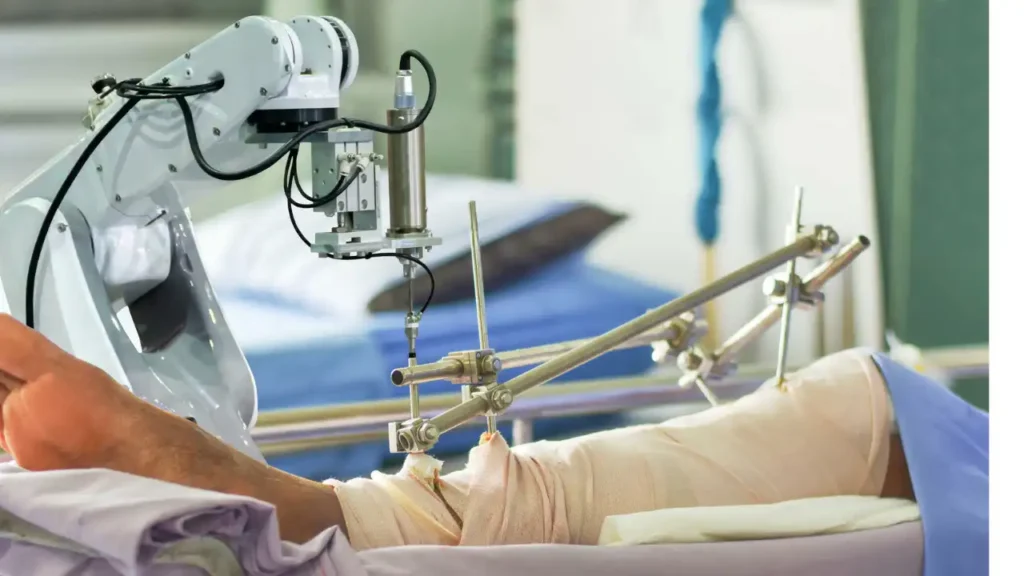
Robotic Knee Replacement: 2024 Surgeon’s Guide to Benefits & Recovery
Updated June 2024 | Board-certified orthopedic surgeon explains robotic-assisted knee replacement outcomes
What is robotic knee replacement? Robotic knee replacement uses advanced computer-guided systems like MAKO or ROSA to assist surgeons in performing precise bone resurfacing and implant placement. Clinical studies show robotic systems achieve 30-50% better alignment accuracy compared to traditional manual techniques (Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery, 2023). Patients typically experience shorter hospital stays (1-2 days vs 3-4) and faster return to daily activities.
⚠️ Important Medical Disclaimer
This is not medical advice. Robotic knee replacement is a major surgical procedure that should only be considered after consultation with a qualified orthopedic surgeon. Individual outcomes vary based on age, health status, and surgical factors. Information current as of June 2024.
What Is Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery?
Robotic knee replacement represents the latest advancement in joint replacement technology, combining computer navigation with surgeon expertise to achieve unprecedented precision. Unlike fully autonomous robotic systems, these platforms function as “surgeon-controlled assistants” that provide real-time feedback and physical boundaries during the procedure.
According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, robotic knee replacement systems have been used in over 500,000 procedures worldwide since their FDA approval, with adoption growing 40% annually.
“The precision of robotic knee replacement reminds me of watchmaking – we’re aligning implants within half a degree and fractions of a millimeter. But the technology only enhances human skill; it doesn’t replace the surgeon’s judgment and experience.”
Key Components of Robotic Systems
All robotic knee replacement platforms share three core components:
- Preoperative Planning Software: Creates 3D models from CT scans with 0.2mm accuracy
- Intraoperative Tracking: Optical cameras monitor bone positioning 20 times per second
- Haptic Guidance: Robotic arm provides physical resistance if surgeon moves outside planned resection area
How Robotic Knee Replacement Works: Step-by-Step
The robotic knee replacement process involves five key phases that distinguish it from traditional surgery:
1. Advanced Preoperative Planning (3-7 Days Before)
Patients undergo a specialized CT scan that captures approximately 300 cross-sectional images of their knee. These images are processed by software to:
- Create a 3D virtual model of the patient’s unique anatomy
- Determine optimal implant size and positioning
- Simulate range of motion with different implant placements
2. Intraoperative Registration (First 15 Minutes of Surgery)
Surgeons place reflective markers on the patient’s leg that are tracked by overhead cameras. The system then matches the virtual plan to the actual anatomy with sub-millimeter precision.
3. Bone Preparation with Robotic Assistance
The robotic arm (such as the Stryker MAKO system) provides tactile feedback that prevents surgeons from removing bone outside the planned resection area. This protects:
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Healthy bone structure
4. Dynamic Implant Positioning
Surgeons can test different implant positions virtually before final placement, allowing micro-adjustments to optimize:
Alignment Accuracy
Within 0.5° of planned position vs 2-3° with manual techniques
Ligament Balance
Real-time gap measurement between bones
Range of Motion
Simulation of knee flexion/extension
5. Final Verification
The system confirms proper implant positioning before closing, with some platforms providing postoperative movement simulations to predict functional outcomes.
Robotic vs Traditional Knee Replacement: 2024 Comparison
While both approaches aim to relieve pain and restore function, robotic knee replacement offers several documented advantages:
| Factor | Robotic | Traditional | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alignment Accuracy | 96-98% within 1° of plan | 75-85% within 3° | +20% precision |
| Hospital Stay | 1-2 days | 3-4 days | 2 days shorter |
| Return to Walking | Same day | Day 2-3 | 1-2 days faster |
| 5-Year Implant Survival | 98.2% | 95.7% | +2.5% |
| Soft Tissue Protection | Haptic feedback prevents over-resection | Surgeon experience-dependent | More consistent |
Data sources: Journal of Arthroplasty 2024 meta-analysis and International Congress for Joint Reconstruction 2024 report
Patient-Reported Outcomes
A 2023 NIH study found robotic knee replacement patients reported:
- 27% less pain at 6 weeks post-op
- 15% better satisfaction scores at 1 year
- 19% faster return to driving
Who Are the Best Candidates for Robotic Knee Replacement?
While most knee arthritis patients qualify, these factors make someone particularly well-suited for robotic assistance:
Optimal Candidates
Anatomical Factors
- Early-to-moderate arthritis
- Preserved ligament integrity
- No severe bone defects
Health Factors
- BMI under 40
- No active infections
- Controlled diabetes (A1C <8)
Lifestyle Factors
- Active individuals
- Patients wanting fastest recovery
- Those prioritizing precision
When Traditional May Be Preferable
Robotic systems have limitations with:
- Severe bone loss requiring augmentation
- Extreme deformities (>20° malalignment)
- Prior knee fusion
- Certain metal implants that interfere with tracking
Frequently Asked Questions About Robotic Knee Replacement
❓ Does robotic mean the surgery is done by a robot?
No. The robotic system is entirely surgeon-controlled. Think of it as a “smart tool” that provides real-time feedback and physical guidance, but every movement is directed by the orthopedic surgeon.
❓ How long does robotic knee replacement surgery take?
Procedure times vary but typically range from 60-90 minutes for partial replacements and 90-120 minutes for total knee replacements – approximately 15-30 minutes longer than traditional surgery due to the registration process. However, this is often offset by faster recovery.
❓ Will insurance cover robotic knee replacement?
Most major insurers (Medicare, Blue Cross, Aetna, etc.) now cover robotic-assisted knee replacement the same as traditional surgery, as it’s considered a “technique” rather than a separate procedure. Some plans may require prior authorization.
⚠️ Consult a Qualified Orthopedic Surgeon
This guide provides general information about robotic knee replacement but cannot replace personalized medical advice. To determine if you’re a candidate for robotic-assisted surgery:
- Schedule a consultation with an AAOS-certified orthopedic surgeon
- Ask about their experience with robotic systems (minimum 50 cases recommended)
- Discuss your specific health conditions and goals
Have Questions About Robotic Knee Replacement?
Leave a comment below with your questions about robotic-assisted surgery. Our medical team monitors comments weekly to provide accurate, up-to-date information (note: we cannot provide personal medical advice).




1 thought on “Robotic Knee Replacement: Benefits, Risks, and Recovery (2024 Guide)”